Medical Care for OI
Related Conditions • Overview
• Prone to OI
– CFS
– Prolonged ICU Stays
• Associated with OI
• Secondary to OI
Conditions Associated With or Contributing to OI
Other medical conditions can affect orthostatic intolerance symptoms and the conditions that cause NMH and POTS. They might require medications that interact or set off OI symptoms. They could also affect the blood pressure and pulse system. Some have more of their effect because they can decrease activity, interfere with an activity routine and even increase prolonged bedrest. .
Knowing how these conditions affect orthostatic symptoms and conditions is the first step. The next step is recognizing when they are active or what makes them active. You can learn more about how to prevent them from flaring. You can also learn how to take steps to get them under control as quickly as you can so they don't affect OI.
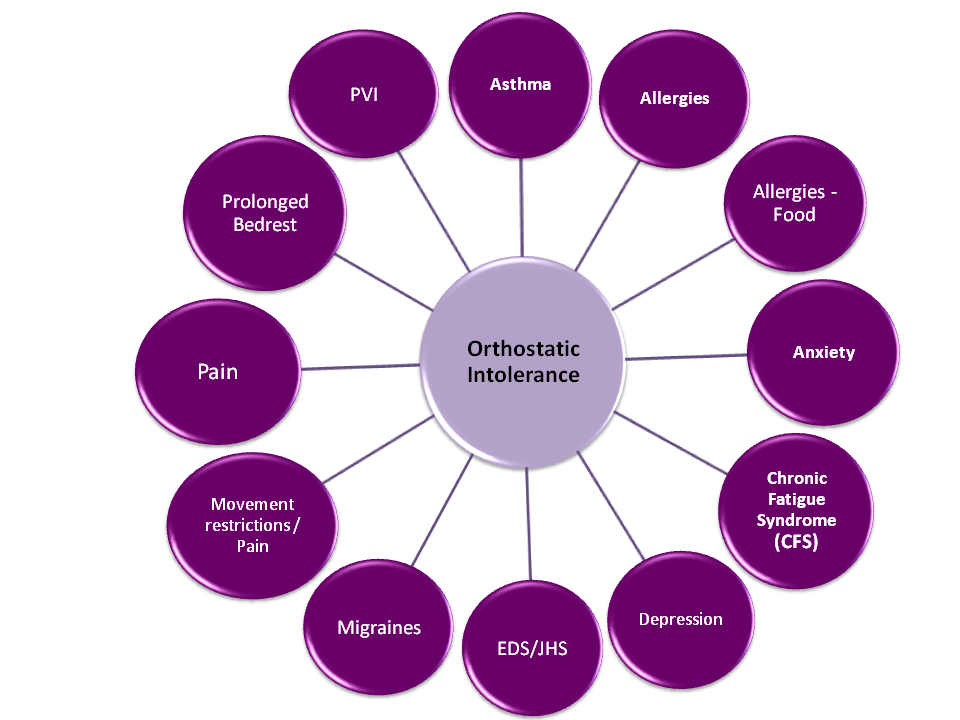
*EDS-Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. JHS-Joint Hypermobility Syndrome. PVI-Pelvic Vein Incompetence
Because of their importance and their impact on people with orthostatic intolerance, two of the conditions are addressed as separate topics: Prolonged Bedrest - See Bedrest and Bedrest & OI. For more on OI and CFS, check out: CFS: OI, POTS & NMH.
![]() AUTHOR's NOTE: We are developing more information on these conditions & suggestions for management to minimize their impact on OI.
AUTHOR's NOTE: We are developing more information on these conditions & suggestions for management to minimize their impact on OI.
To find out when new material is added. Follow us on Twitter ![]() or Facebook
or Facebook
General References:
- Rowe, Peter. Managing Orthostatic Intolerance. Webinar. September 1, 2010. Hosted by CFIDS Association of American. Accessed June 1, 2012. Written material. Slides PDF. Video
- Johnson JN, Mack KJ, Kuntz NL, Brands CK, Porter CJ and Fischer PR. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome: A Clinical Review. Pediatr Neuro 2010; 42:77-85. Abstract.
- Lapp, Charles. Treating CFS & FM: The Stepwise Approach. Webinar - CFIDS.org. May 20, 2010. Video. Slides. Slides with notes. Last Accessed June 30, 2012.
Author: Kay E. Jewell, MD
Page Last Updated: July 5, 2012
